As per Statisa, there are a total of 15.14 Billion connected IoT devices in 2023 globally, and this number is expected to cross 29 Billion by 2030.
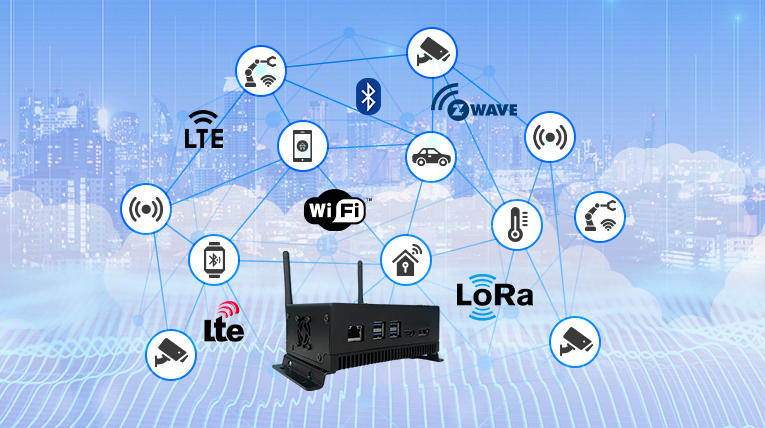
Ever wondered how these devices communicate with each other and the external world? There is a central hub, or IoT Gateway, that serves as a bridge between the devices and the cloud, allowing for communication, data collection, and data processing.
In this blog, we will deep dive to understand what is an IoT gateway, key components to keep in mind while designing, benefits and use cases of using IoT gateways and how VVDN can help customers who are looking for a reliable and secure IoT gateway for their next- gen application.
What is an IoT Gateway? and how does it actually work?
An IoT gateway is a device that sits between the Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the cloud, allowing them to exchange data, perform analytics, and take actions based on the data collected.
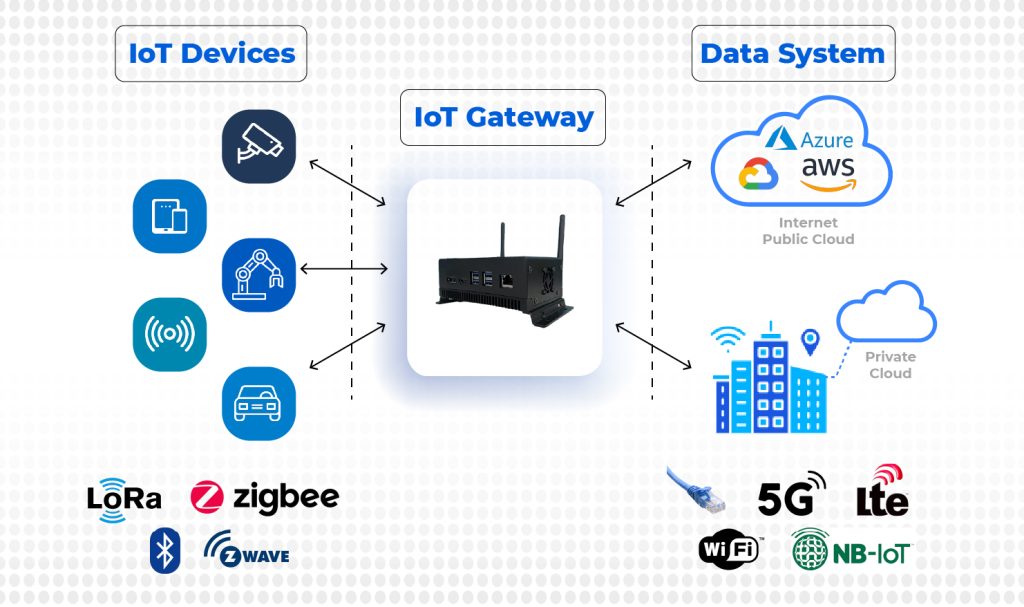
The key components of IoT gateway engineering include:
- Hardware Design: This involves designing the physical components of the gateway, such as the circuit board, power supply, and networking interfaces.
- Software Development: This involves creating the firmware and software that runs on the gateway, including the operating system, drivers, and communication protocols.
- Mechanical: Designing the mechanical of the gateway also becomes important in terms of ruggedness, IP rating, etc to make it ideal for installing in harsh environments operating over a wide temperature range.
- Security: Since IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, security is a critical component of IoT gateway engineering. Engineers must design the gateway with security in mind and implement appropriate security measures such as encryption, authentication, and access control.
- Connectivity: The gateway should have multiple connectivity options both wired and wireless such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Cellular (LTE, 4G, 5G), Bluetooth, and Zigbee, LoRa, etc to connect to different devices and transmission of data in real time.
- Integration: IoT gateways must be able to integrate with a wide range of devices and software platforms. Engineers must design the gateway to be compatible with various sensors, devices, and cloud platforms, as well as APIs and communication protocols.
- Testing and Validation: Engineers must test and validate the IoT gateway to ensure that it functions properly and meets the desired performance requirements. This includes stress testing, functional testing, and interoperability testing.
Evolution of IoT Gateways:
In the past, gateways were designed only to facilitate communication and send the data to the cloud for further analytics and decision making. They do not support performing analytics on the edge. Nowadays, edge gateways are gaining popularity across the globe. They have the capability to perform all analytics on the edge without sending the data to the cloud which eventually reduces latency and improves response times, making IoT applications more responsive. With enabling 5G connectivity to these gateways, it can further help in gaining quick insights, automate and instantly give updates about the connected devices and sensors in real time.
Here are some benefits of using an IoT gateway:
- Data Aggregation: An IoT gateway can aggregate data from multiple IoT devices including sensors, cameras, etc, process it, and send it to the cloud for analysis. This can help reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, making it more efficient and reducing costs.
- Security: An IoT gateway can act as a firewall, protecting IoT devices from cyberattacks. It can also encrypt data as it is transmitted to the cloud, ensuring that data is protected from unauthorized access.
- Edge Computing: An IoT gateway can perform some processing at the edge, reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud. This can help reduce latency and improve response times, making IoT applications more responsive.
- Interoperability: An IoT gateway can provide a common interface between different types of IoT devices, making it easier to integrate new devices into an existing system.
- Scalability: An IoT gateway can help scale IoT deployments by providing a centralized management point for large numbers of IoT devices.
Use cases for IoT gateway:
An IoT gateway can help improve the efficiency, security, and reliability of IoT systems, making them more useful and effective for businesses and consumers. IoT gateways can be used in various use cases to connect and manage IoT devices. Here are some examples of IoT gateway use cases:
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industrial environments or factories, an IoT gateway can be used to connect different types of sensors and devices, collect data from them, and transmit it to the cloud for analysis. This can help optimize industrial processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
- Retail : In the retail industry, edge gateways are in high demand and can be used to know the consumer buying behavior, taste, needs and habits in real time.
- Smart City: IoT Gateways can be used in smart cities applications to collect the data from various sensors installed, cameras, etc and take action accordingly by processing the information either on edge or cloud.
- Transportation: In the transportation industry, an IoT gateway can be used to collect data from vehicles, including speed, location, and engine performance. This data can be used to optimize routes, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
- Smart Home: In a smart home, an IoT gateway can act as a central hub, connecting various smart devices like lights, thermostats, and security cameras. The gateway can then process and analyze the data collected from these devices and take appropriate actions, such as adjusting the temperature or turning on the lights.
- Agriculture: In agriculture, an IoT gateway can be used to collect data from soil sensors, weather stations, and other agricultural devices. This data can then be analyzed to optimize crop growth and increase yields.
- Healthcare: An IoT gateway can be used in healthcare settings to monitor patient health and collect data from medical devices like blood glucose monitors and blood pressure cuffs. This data can then be transmitted to healthcare providers for analysis and used to improve patient outcomes.
Overall, IoT gateways can be used in a wide variety of industries and settings to connect and manage IoT devices, collect and process data, and improve efficiency and effectiveness.
How VVDN can help its customers looking for IoT Gateways:
VVDN supports global OEMs, system integrators with our unique expertise in designing, developing and manufacturing tailored made IoT gateways as per the requirement. In the past, VVDN has designed, developed and manufactured IoT gateways based on different platforms including NXP, NVIDIA, Qualcomm, Intel, AMD-Xilinx, Kinara, etc that are currently deployed on the field for different use cases.
If you are also looking to design an IoT gateway, understand how we can help and what real-life industry knowledge we can bring to the table. Contact VVDN today at info@vvdntech.com.